Dying of Covid in a ‘Separate and Unequal’ L.A. Hospital
Inside an overwhelmed facility in the worst-hit part of California, where the patriarchs of two immigrant families were taken when they fell sick.
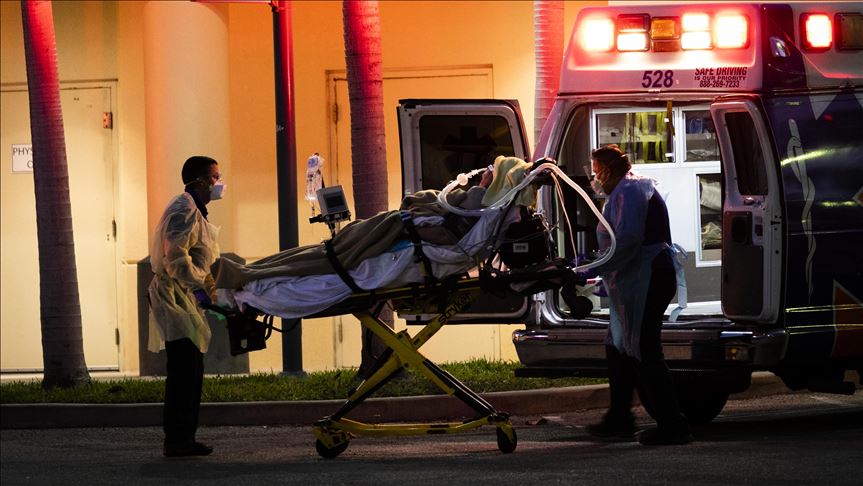
LOS ANGELES — Over the New Year’s holiday, the grown children of two immigrant families called 911 to report that their fathers were having difficulty breathing. The men, born in Mexico and living three miles from each other in the United States, both had diabetes and high blood pressure. They both worked low-wage, essential jobs — one a minibus driver, the other a cook. And they both hadn’t realized how sick they were.
Three weeks later, the men — Emilio Virgen, 63, and Gabriel Flores, 50 — both died from Covid-19. Their stories were hauntingly familiar at Martin Luther King Jr. Community Hospital, by size the hardest-hit hospital in the hardest-hit county in the state now leading the nation in cases and on the brink of surpassing New York with the highest death toll. In the intensive care unit on Jan. 21, Mr. Virgen became No. 207 on the hospital’s list of Covid-19 fatalities; Mr. Flores, just down the hall, became No. 208.
The New York Times spent more than a week inside the hospital, during a period when nearly a quarter of all Covid inpatients there were dying, despite advances in knowledge of the disease. It was an outcome that approached that of some New York hospitals last spring, when the city was the epicenter of the coronavirus pandemic. That rise coincided with a surge of cases in Southern California, a doubling of the mortality rate in Los Angeles hospitals over all and the spread of a new local strain that may be more transmissible than the more prevalent one.
Dying of Covid in a ‘Separate and Unequal’ L.A. Hospital
Eight out of ten of those who died at M.L.K. hospital were Hispanic, a group with the highest Covid-19 death rates in Los Angeles County, followed by Black residents. County data also showed that the most impoverished Los Angeles residents, many of them around the hospital in South Los Angeles, are dying of the disease at four times the rate of the wealthiest.
Michelle Goldson, an I.C.U. nurse who cared for both Mr. Virgen and Mr. Flores, said many patients had a “distrust of the health care system, distrust of doctors” and came in only when desperately ill. Severe cases, she said, weren’t limited to older people. “Everybody’s dying here,” she said. As she headed home one recent evening, she waved at a 27-year-old patient who was sitting up eating dinner. When she returned the next morning, he was dead. “What kind of virus is this?” she asked.
Right now, it is one that is merciless in dense, low-income neighborhoods like those where Mr. Virgen and Mr. Flores lived. Relatives similarly described them as hardworking and upbeat, determined to provide for their families. Mr. Virgen raised four children who all went to college, and stubbornly nurtured scrawny mango and lemon trees. Mr. Flores was proud that his oldest son, a Dreamer who had been slipped into the country as a toddler, had graduated from the Los Angeles police academy.
For M.L.K.’s chief executive, Dr. Elaine Batchlor, the inequities in disease and death from Covid reflect those long present in the community. Patients come from what she termed a “medical desert,” with chronic shortages of primary care doctors and other health services.







